WebGL(TypeScript)--- 立方体描画&回転
下記記事にて、WebGLを用いて三角形を描画しました。
WebGL(TypeScript)--- 三角形描画 - 何でもプログラミング
今回は引き続き、立方体を描画&回転を実装してみたいと思います。
上記記事をベースに実装していきますので、解説のない部分は参照をお願いいたします。
Index Buffer作成関数
今回はIndex Bufferを用いて描画を行ってみたいと思います。
ですので、作成関数を準備します。
function createIndexBuffer(gl : WebGLRenderingContext, indices : number[]) : WebGLBuffer { const buffer = gl.createBuffer()!; gl.bindBuffer(gl.ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER, buffer); gl.bufferData(gl.ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER, new Uint16Array(indices), gl.STATIC_DRAW); return buffer; }
Matrix4クラス
回転を実現するため、最低限の行列クラスを準備します。
回転行列を作成するrotate関数、転置を行うtranspose関数(WebGLは列優先のため)、左上の3x3行列を取り出すgetMatrix3Data関数(法線変換用)を定義しています。
class Matrix4 { constructor(readonly data: number[]) { } transposed() : Matrix4 { return new Matrix4([ this.data[0], this.data[4], this.data[8], this.data[12], this.data[1], this.data[5], this.data[9], this.data[13], this.data[2], this.data[6], this.data[10], this.data[14], this.data[3], this.data[7], this.data[11], this.data[15], ]); } getMatrix3Data() : number[] { return [ this.data[0], this.data[1], this.data[2], this.data[4], this.data[5], this.data[6], this.data[8], this.data[9], this.data[10], ]; } static rotate(degree : number, x : number, y : number, z : number) : Matrix4 { const length = Math.sqrt(x * x + y * y + z * z); x /= length; y /= length; z /= length; const radian = degree * Math.PI / 180.0; const s = Math.sin(radian); const c = Math.cos(radian); return new Matrix4([ x * x * (1 - c) + c, x * y * (1 - c) - z * s, z * x * (1 - c) + y * s, 0, x * y * (1 - c) + z * s, y * y * (1 - c) + c, y * z * (1 - c) - x * s, 0, z * x * (1 - c) - y * s, y * z * (1 - c) + x * s, z * z * (1 - c) + c, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1 ]); } }
main関数
ライティングを行うShaderの作成と、立方体のVertex Buffer&Index Bufferの作成を行い、requestAnimationFrameにて回転させつつ描画を行っています。
実行すると下記のような表示になります。(実際はアニメーションします。)

let gl : WebGLRenderingContext; function main() : void { const canvas = <HTMLCanvasElement>document.getElementById("gl"); gl = canvas.getContext("webgl")!; // Vertex Shader(頂点と法線を変換して次へ) const vertexCode = ` attribute vec4 position; attribute vec3 normal; uniform mat4 matrix; uniform mat3 normalMatrix; varying vec3 v_normal; void main() { gl_Position = matrix * position; v_normal = normalMatrix * normal; } `; // Fragment Shader(ライティングを行って描画) const fragmentCode = ` precision mediump float; varying vec3 v_normal; void main() { vec3 light = vec3(0.0, 0.0, -1.0); float g = dot(light, normalize(v_normal)); g = max(0.0, g); gl_FragColor = vec4(0.0, g, 0.0, 1.0); } `; const program = createProgram(gl, vertexCode, fragmentCode); // 立方体定義(頂点、法線) const vertices = [ 0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, -0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.5, -0.5, 0.5, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, -0.5, -0.5, 0.5, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.5, 0.5, -0.5, 0.0, 0.0, -1.0, -0.5, 0.5, -0.5, 0.0, 0.0, -1.0, 0.5, -0.5, -0.5, 0.0, 0.0, -1.0, -0.5, -0.5, -0.5, 0.0, 0.0, -1.0, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.5, -0.5, 0.5, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.5, 0.5, -0.5, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.5, -0.5, -0.5, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, -0.5, 0.5, 0.5, -1.0, 0.0, 0.0, -0.5, -0.5, 0.5, -1.0, 0.0, 0.0, -0.5, 0.5, -0.5, -1.0, 0.0, 0.0, -0.5, -0.5, -0.5, -1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.5, 0.5, -0.5, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, -0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, -0.5, 0.5, -0.5, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.5, -0.5, 0.5, 0.0, -1.0, 0.0, 0.5, -0.5, -0.5, 0.0, -1.0, 0.0, -0.5, -0.5, 0.5, 0.0, -1.0, 0.0, -0.5, -0.5, -0.5, 0.0, -1.0, 0.0, ]; const vertexBuffer = createVertexBuffer(gl, vertices); const indices = [ 0, 2, 1, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 5, 7, 6, 8, 10, 9, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 13, 15, 14, 16, 18, 17, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 21, 23, 22, ]; const indexBuffer = createIndexBuffer(gl, indices); // 初期設定 gl.useProgram(program); const positionAttrib = gl.getAttribLocation(program, "position"); const normalAttrib = gl.getAttribLocation(program, "normal"); const matrixUniform = gl.getUniformLocation(program, "matrix")!; const normalMatrixUniform = gl.getUniformLocation(program, "normalMatrix")!; gl.bindBuffer(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, vertexBuffer); gl.enableVertexAttribArray(positionAttrib); gl.enableVertexAttribArray(normalAttrib); gl.vertexAttribPointer(positionAttrib, 3, gl.FLOAT, false, 24, 0); gl.vertexAttribPointer(normalAttrib, 3, gl.FLOAT, false, 24, 12); gl.bindBuffer(gl.ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER, indexBuffer); gl.enable(gl.DEPTH_TEST); gl.enable(gl.CULL_FACE); // デフォルトで反時計回りが表 // 描画関数 let rotation = 0; function step(time : number) : void { rotation++; const mat = Matrix4.rotate(rotation, 1, 1, 1).transposed(); gl.uniformMatrix4fv(matrixUniform, false, mat.data); gl.uniformMatrix3fv(normalMatrixUniform, false, mat.getMatrix3Data()); gl.clearColor(0.8, 0.8, 0.8, 1); gl.clear(gl.COLOR_BUFFER_BIT); gl.drawElements(gl.TRIANGLES, indices.length, gl.UNSIGNED_SHORT, 0); requestAnimationFrame(step); } // 描画スタート requestAnimationFrame(step); } main();
WebGL(TypeScript)--- 三角形描画
今回はWebGLを用いてcanvasに三角形を描画してみたいと思います。
ライブラリを用いず、一から実装してみます。
HTMLの準備
表示のため、下記htmlを用意しました。
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <body> <canvas id="gl_canvas" width="100" height="100"></canvas> <script src="script.js"></script> </body> </html>
Shader作成関数
Vertex ShaderのコードとFragment Shaderのコードから、WebGLProgramを作成する関数を準備します。
function createProgram(gl : WebGLRenderingContext, vertexCode : string, fragmentCode : string) : WebGLProgram { // Vertex Shader コンパイル const vertexShader = gl.createShader(gl.VERTEX_SHADER)!; compileShader(gl, vertexShader, vertexCode); // Fragment Shader コンパイル const fragmentShader = gl.createShader(gl.FRAGMENT_SHADER)!; compileShader(gl, fragmentShader, fragmentCode); // Program作成 const program = gl.createProgram()!; gl.attachShader(program, vertexShader); gl.attachShader(program, fragmentShader); gl.linkProgram(program); // エラー確認 console.log(gl.getProgramInfoLog(program)); if (!gl.getProgramParameter(program, gl.LINK_STATUS)) throw new Error("program error"); return program; }
上記で利用しているcompileShaderは次のようになります。
function compileShader(gl : WebGLRenderingContext, shader : WebGLShader, code : string) : void { gl.shaderSource(shader, code); gl.compileShader(shader); // エラー確認 console.log(gl.getShaderInfoLog(shader)); if (!gl.getShaderParameter(shader, gl.COMPILE_STATUS)) throw new Error("compile error"); }
VertexBuffer作成関数
頂点データの配列からWebGLBufferを作成する関数を準備します。
function createVertexBuffer(gl : WebGLRenderingContext, vertices : number[]) : WebGLBuffer { const buffer = gl.createBuffer()!; gl.bindBuffer(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, buffer); gl.bufferData(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, new Float32Array(vertices), gl.STATIC_DRAW); return buffer; }
main関数
三角形を描画する関数は下記の様になります。
canvasにはこのように描画されます。

let gl : WebGLRenderingContext; function main() : void { const canvas = <HTMLCanvasElement>document.getElementById("gl_canvas"); gl = canvas.getContext("webgl")!; const vertexCode = ` attribute vec4 position; void main() { gl_Position = position; } `; const fragmentCode = ` void main() { gl_FragColor = vec4(0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 1.0); } `; const program = createProgram(gl, vertexCode, fragmentCode); const vertices = [ 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, -1.0, -1.0, 0.0, 1.0, -1.0, 0.0, ]; const vertexBuffer = createVertexBuffer(gl, vertices); gl.useProgram(program); const positionAttrib = gl.getAttribLocation(program, "position"); gl.enableVertexAttribArray(positionAttrib); gl.bindBuffer(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, vertexBuffer); gl.vertexAttribPointer(positionAttrib, 3, gl.FLOAT, false, 0, 0); gl.clearColor(0.3, 0.3, 0.3, 1); gl.clear(gl.COLOR_BUFFER_BIT); gl.drawArrays(gl.TRIANGLES, 0, 3); } main();
Direct2D --- 画像読み込み
Direct2Dにおいて画像ファイルを読み込んで表示する場合、Windows Imaging Component (WIC)を利用します。
今回は実際にそれを実装してみたいと思います。
画像ファイルを32bitRGBAで読み込み
まずIWICImagingFactoryを作成し、factory経由でデコードを行います。
また32bitRGBAに変換するため、IWICFormatConverterを利用します。
#include <wincodec.h> #include <wrl\client.h> using namespace Microsoft::WRL; ComPtr<IWICBitmapSource> WICBitmapFromFile(wchar_t* path) { ComPtr<IWICImagingFactory> factory; AssertHR(CoCreateInstance( CLSID_WICImagingFactory, NULL, CLSCTX_INPROC_SERVER, IID_PPV_ARGS(&factory) )); ComPtr<IWICBitmapDecoder> decoder; AssertHR(factory->CreateDecoderFromFilename( path, NULL, GENERIC_READ, WICDecodeMetadataCacheOnDemand, &decoder )); ComPtr<IWICBitmapFrameDecode> frame; AssertHR(decoder->GetFrame(0, &frame)); // 32bit RGBAに変換 ComPtr<IWICFormatConverter> converter; AssertHR(factory->CreateFormatConverter(&converter)); AssertHR(converter->Initialize( frame.Get(), GUID_WICPixelFormat32bppPBGRA, WICBitmapDitherTypeNone, NULL, 0.0f, WICBitmapPaletteTypeCustom )); return converter; }
Direct2Dアプリケーションで利用
ID2D1RenderTargetのDrawBitmapを利用して描画します。
ComPtr<ID2D1Bitmap> image = WICBitmapFromFile(L"Parrots.bmp"); renderTarget->DrawBitmap(image.Get(), D2D1::RectF(0, 0, width, height));
ただしWICを利用するに際し、アプリケーションの始めにCoInitializeを呼んでおく必要があります。
AssertHR(CoInitialize(NULL));
...
CoUninitialize();
Direct2Dの基本的な使い方は下記を参照してみてください。
Direct2D導入(ID2D1HwndRenderTarget) - 何でもプログラミング
Direct2D導入(ID2D1DeviceContext) - 何でもプログラミング
SDL導入
画像処理コードの確認の際、C++で簡単にウィンドウを表示したいと思い、SDLを少し使ってみました。
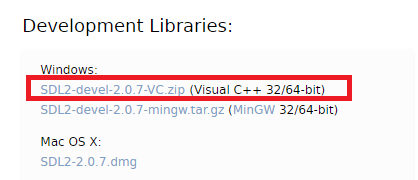
SDLダウンロード
下記ページよりdllをダウンロードします。
Simple DirectMedia Layer - SDL version 2.0.7 (stable)
shared_ptrに変換する関数定義(任意)
SDLはCのライブラリのため、ポインタの開放は手動でやる必要があります。(例:SDL_CreateWindow → SDL_DestroyWindow)
ポインタの管理を楽にするため、shared_ptrに変換する関数を準備します。
shared_ptr作成時に対応するデストラクタを渡すようにしています。
#define DEEFINE_TO_SHARED_PTR(type, destructor) std::shared_ptr<type> ToSharedPtr(type* p) { return std::shared_ptr<type>(p, destructor); } DEEFINE_TO_SHARED_PTR(SDL_Window, SDL_DestroyWindow) DEEFINE_TO_SHARED_PTR(SDL_Renderer, SDL_DestroyRenderer) DEEFINE_TO_SHARED_PTR(SDL_Surface, SDL_FreeSurface) DEEFINE_TO_SHARED_PTR(SDL_Texture, SDL_DestroyTexture)
簡単な実装
画像を読み込んで表示するアプリケーションを実装してみます。
ついでにマウスの位置に正方形も描画してみます。

#include <SDL.h> #pragma comment(lib, "SDL2.lib") #pragma comment(lib, "SDL2main.lib") int main(int, char**) { SDL_assert(SDL_Init(SDL_INIT_VIDEO) == 0); std::shared_ptr<SDL_Window> window = ToSharedPtr(SDL_CreateWindow( "SDL Sample", SDL_WINDOWPOS_UNDEFINED, SDL_WINDOWPOS_UNDEFINED, 640, 480, 0 )); SDL_assert(window); std::shared_ptr<SDL_Renderer> renderer = ToSharedPtr(SDL_CreateRenderer(window.get(), -1, 0)); SDL_assert(renderer); std::shared_ptr<SDL_Surface> surface = ToSharedPtr(SDL_LoadBMP("Parrots.bmp")); SDL_assert(surface); std::shared_ptr<SDL_Texture> texture = ToSharedPtr(SDL_CreateTextureFromSurface(renderer.get(), surface.get())); SDL_assert(texture); while (1) { SDL_Event event; if (SDL_PollEvent(&event) == 0) continue; if (event.type == SDL_QUIT) break; else if (event.type == SDL_MOUSEMOTION) { SDL_assert(SDL_RenderClear(renderer.get()) == 0); // 画像描画 SDL_assert(SDL_RenderCopy(renderer.get(), texture.get(), nullptr, nullptr) == 0); // マウスの位置に正方形描画 SDL_Rect rect = { event.motion.x, event.motion.y, 50, 50 }; SDL_assert(SDL_SetRenderDrawColor(renderer.get(), 255, 255, 255, 255) == 0); SDL_assert(SDL_RenderFillRect(renderer.get(), &rect) == 0); SDL_RenderPresent(renderer.get()); } } SDL_Quit(); return 0; }
複数のキーを利用できるConditionalWeakTableクラス
下記記事にて、2つのキーを利用できるWeakTableを実装してみました。
2つのキーを利用できるConditionalWeakTableクラス - 何でもプログラミング
今回は3,4個と拡張しやすいように、複数個のキーを利用できるWeakTableを実装してみたいと思います。
Keysクラス
前回は2つのWeakReferenceプロパティをもっていましたが、今回はWeakReference配列を扱うよう変更しました。
EqualsとGetHashCodeを、WeakReferenceではなくTargetで行うところは変わっていません。
class Keys { public WeakReference[] WeakKeys { get; } int _hash; public bool IsAlive() { return WeakKeys.All(x => x.IsAlive); } public Keys(object[] keys) { WeakKeys = keys.Select(x => new WeakReference(x)).ToArray(); _hash = keys.Aggregate(365011897, (hash, key) => hash * -1521134295 + key.GetHashCode()); } public override bool Equals(object obj) { var keys = obj as Keys; return keys != null && WeakKeys.Length == keys.WeakKeys.Length && WeakKeys.Zip(keys.WeakKeys, TargetEquals).All(x => x); } bool TargetEquals(WeakReference weakRef1, WeakReference weakRef2) { var ref1 = weakRef1.Target; var ref2 = weakRef2.Target; return ref1 != null && ref2 != null && Equals(ref1, ref2); } public override int GetHashCode() { return _hash; } }
WeakTableクラス
まず、一般的はkey配列に対応したクラスを作成します。
class WeakTable<TValue> { object _lockObj = new object(); Dictionary<Keys, TValue> _dictionary = new Dictionary<Keys, TValue>(); public WeakTable() { WeakEventManager<GCNotifier, EventArgs>.AddHandler(null, nameof(GCNotifier.Collected), (s, e) => CheckReferences()); } public void Add(object[] keys, TValue value) { lock (_lockObj) { _dictionary[new Keys(keys)] = value; } } public bool TryGetValue(object[] keys, ref TValue value) { lock (_lockObj) { var key = new Keys(keys); if (_dictionary.ContainsKey(key) == false) return false; value = _dictionary[key]; return true; } } public void CheckReferences() { lock (_lockObj) { _dictionary = _dictionary .Where(x => x.Key.IsAlive()) .ToDictionary(x => x.Key, x => x.Value); } } }
これを利用して、例えば2つのキーのWeakTableは下記のように定義します。
class WeakTable<TKey1, TKey2, TValue> where TKey1 : class where TKey2 : class { WeakTable<TValue> _table = new WeakTable<TValue>(); public void Add(TKey1 key1, TKey2 key2, TValue value) => _table.Add(new object[] { key1, key2 }, value); public bool TryGetValue(TKey1 key1, TKey2 key2, ref TValue value) => _table.TryGetValue(new object[] { key1, key2 }, ref value); }
2つのキーを利用できるConditionalWeakTableクラス
.NETのConditionalWeakTableは、キーを弱参照で保持し、キーがGCされたときに自動でキーと値がRemoveされるようになっています。
しかし、キーとして複数の参照を持ち、参照のうちどれかがGCされたらRemoveを行うといった使い方はできません。
今回は複数の参照キーを指定できるConditionalWeakTableのようなものを実装してみたいと思います。
ConditionalWeakTableの中身
内部的にDependentHandleという構造体で管理しているようですが、privateのため利用できません。
Ephemeronというデータ構造を利用しているらしいですが、詳しくは追及していません。
2つのキーを弱参照で保持するクラス
Keyを弱参照で保持し、EqualsやGetHashCodeをもともとのKeyから算出するクラスを作成します。
class Keys { public WeakReference<TKey1> Key1 { get; } public WeakReference<TKey2> Key2 { get; } int _hash; public bool IsAlive() { return Key1.TryGetTarget(out var key1) && Key2.TryGetTarget(out var key2); } public Keys(TKey1 key1, TKey2 key2) { Key1 = new WeakReference<TKey1>(key1); Key2 = new WeakReference<TKey2>(key2); // WeakReferenceではなく、もとのkeyからhash作成 _hash = 365011897; _hash = _hash * -1521134295 + key1.GetHashCode(); _hash = _hash * -1521134295 + key2.GetHashCode(); } public override bool Equals(object obj) { // WeakReferenceの比較ではなく、中身の参照の比較 var keys = obj as Keys; return keys != null && TargetEquals(Key1, keys.Key1) && TargetEquals(Key2, keys.Key2); } bool TargetEquals<T>(WeakReference<T> weakRef1, WeakReference<T> weakRef2) where T : class { return weakRef1.TryGetTarget(out var ref1) && weakRef2.TryGetTarget(out var ref2) && Equals(ref1, ref2); } public override int GetHashCode() { return _hash; } }
WeakTableクラス
上記のKeysクラスを利用して、WeakTable本体を実装していきます。
class WeakTable<TKey1, TKey2, TValue> where TKey1 : class where TKey2 : class { Dictionary<Keys, TValue> _dictionary = new Dictionary<Keys, TValue>(); public void Add(TKey1 key1, TKey2 key2, TValue value) { _dictionary[new Keys(key1, key2)] = value; } public bool TryGetValue(TKey1 key1, TKey2 key2, ref TValue value) { var key = new Keys(key1, key2); if (_dictionary.ContainsKey(key) == false) return false; value = _dictionary[key]; return true; } public void CheckReferences() { // 不必要なレコードを削除 _dictionary = _dictionary .Where(x => x.Key.IsAlive()) .ToDictionary(x => x.Key, x => x.Value); } }
GCが行われたときにCheckReferencesを呼ぶ
現状のままでは、利用者がCheckReferencesを呼ばないと不必要なレコードが解放されないので、GC時に呼ばれるよう実装してみます。
GCの検知の詳細は下記記事を参照してみてください。
Garbage Collectionを検知する(C#) - 何でもプログラミング
今回はこのようなクラスを用意しました。
class GCNotifier { public static event EventHandler Collected; static GCNotifier() { new DummyObject(); } class DummyObject { ~DummyObject() { if (!AppDomain.CurrentDomain.IsFinalizingForUnload() && !Environment.HasShutdownStarted) { Collected?.Invoke(null, EventArgs.Empty); new DummyObject(); } } } }
GCNotifierを利用して、WeakTableに実装を追加します。
WeakEventManagerでCollectedにアタッチし、lock機構を追加しています。
class WeakTable<TKey1, TKey2, TValue> where TKey1 : class where TKey2 : class { object _lockObj = new object(); Dictionary<Keys, TValue> _dictionary = new Dictionary<Keys, TValue>(); public WeakTable() { WeakEventManager<GCNotifier, EventArgs>.AddHandler(null, nameof(GCNotifier.Collected), (s, e) => CheckReferences()); } public void Add(TKey1 key1, TKey2 key2, TValue value) { lock (_lockObj) { _dictionary[new Keys(key1, key2)] = value; } } public bool TryGetValue(TKey1 key1, TKey2 key2, ref TValue value) { lock (_lockObj) { var key = new Keys(key1, key2); if (_dictionary.ContainsKey(key) == false) return false; value = _dictionary[key]; return true; } } public void CheckReferences() { lock (_lockObj) { _dictionary = _dictionary .Where(x => x.Key.IsAlive()) .ToDictionary(x => x.Key, x => x.Value); } } }
Garbage Collectionを検知する(C#)
通常のプログラミングにおいて、いつGCされたか気にする必要はありませんが、極まれにGCのタイミングで処理をしたい時があります(設計で回避するべきではありますが…)
今回はGCを検知する方法を調べてみました。
GC.WaitForFullGCComplete
GCクラスの関数を利用する方法です。
これを利用するには、App.configで下記が指定されている必要があります。(コンカレントGCを無効化)
<configuration> <runtime> <gcConcurrent enabled="false" /> </runtime> </configuration>
GCNotifierクラスを定義してみます。
GC.RegisterForFullGCNotificationで通知を有効化し、GC.WaitForFullGCApproachとGC.WaitForFullGCCompleteで通知を待ちます。
GC.RegisterForFullGCNotificationの引数は、大きいほど通知を受け取りやすくなるそうです。
static class GCNotifier { public static event Action Collected; public static void Start() { GC.RegisterForFullGCNotification(10, 10); Task.Run(() => { while (true) { GC.WaitForFullGCApproach(); if (GC.WaitForFullGCComplete() == GCNotificationStatus.Succeeded) Collected?.Invoke(); } }); } }
利用は下記のようになります。
GCNotifier.Collected += () => Console.WriteLine("collected");
GCNotifier.Start();
Finalizeを利用
下記のものを簡略化してみます。
Jeffrey Richter: Receiving notifications when garbage collections occur – Microsoft Press blog
DummyクラスのFinalizeでコールバックを呼び、さらに新しいDummyオブジェクトを生成しています。
GCNotifierクラスは下記のようになり、利用方法はGC.WaitForFullGCCompleteの時と同じです。
static class GCNotifier { public static event Action Collected; public static void Start() { new DummyObject(); } class DummyObject { ~DummyObject() { if (!AppDomain.CurrentDomain.IsFinalizingForUnload() && !Environment.HasShutdownStarted) { Collected?.Invoke(); new DummyObject(); } } } }